Roles & Permissions
Please note that Storyblok's documentation is currently undergoing major restructuring. Most resources can now be found on the dedicated documentation platform. This resource and others will be updated and moved shortly.
Roles are for giving specific permissions to various users in your space. It provides owners and admins greater control over who can publish what, especially for bigger projects. For instance, if you have several authors on your blog, you can give different access permissions to each author. This would minimize the risk of authors getting in each other’s way and provide a robust solution to organizing team coordination.
What are Roles?
Default Roles
Your Storyblok space is set up with three roles by default: Owner, Admin, and Editor.
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Owner | The user who created the space; can create, update, delete roles and grant permissions. Can also create and update content. |
| Admin | Creates and grants permissions to each custom role. Admin manages users and creates/updates content. |
| Editor | A role that has some limitations by default. This is meant to provide convenience for the user in case they are unsure of what permissions to grant. Editors can create and update content, but cannot manage other users. |
Custom Roles
Besides the default roles of Editor and Admin, you are free to create any roles that meet your team's needs. The user creates custom roles to further tailor your experience and manage your team and spaces on Storyblok. You may have designers, translators, or content creators who will not need access to the entire project but rather specific parts of it. This is where custom roles and permissions come in handy.
What are Permissions?
Permissions are rules set within a role that either grant or prevent access to certain aspects of the space.
Permission Types
It is possible to manage permissions at a granular level with Storyblok. This allows you to have more control over your workflow as your team increases in size and variety of roles. For instance, you can have an "English Author" role that only has access to content in the English language, and they will not be able to publish in any other language accidentally.
General
Besides their role as Editors, there is no pre-defined set of permissions you have to use-- you have the freedom to define the level of access for each role depending on your needs.
| Type | What it involves |
|---|---|
| Content & Editor | This category encompasses tasks related to managing content, including reading, saving, and publishing it. Specifically, it involves functionalities such as deploying to pipelines, accessing an image or visual editor, and handling Stories by enabling actions like moving a story or altering its slug. Administrators also can grant permissions for hiding content or folders. Additionally, there are options available for managing access to both Draft and Published JSON on custom roles. |
| Tags | the management of tags: creating, updating, and deleting |
| Datasources | allowing the editing of datasource keys and values |
| eCommerce app | granting the user access to the eCommerce app |
| Task app | granting the user access to the Task app |
Content
For these permissions, the user has access/rights to edit, view, or deploy if nothing is specified.
| Type | What it involves |
|---|---|
| Languages | access to specific languages, i.e., restricting a user’s access to content in English, Spanish, French, etc. |
| Pipelines | restricts access to specific pipelines that this particular role can deploy to |
| Folder/content item | restricts access to specific folders/content |
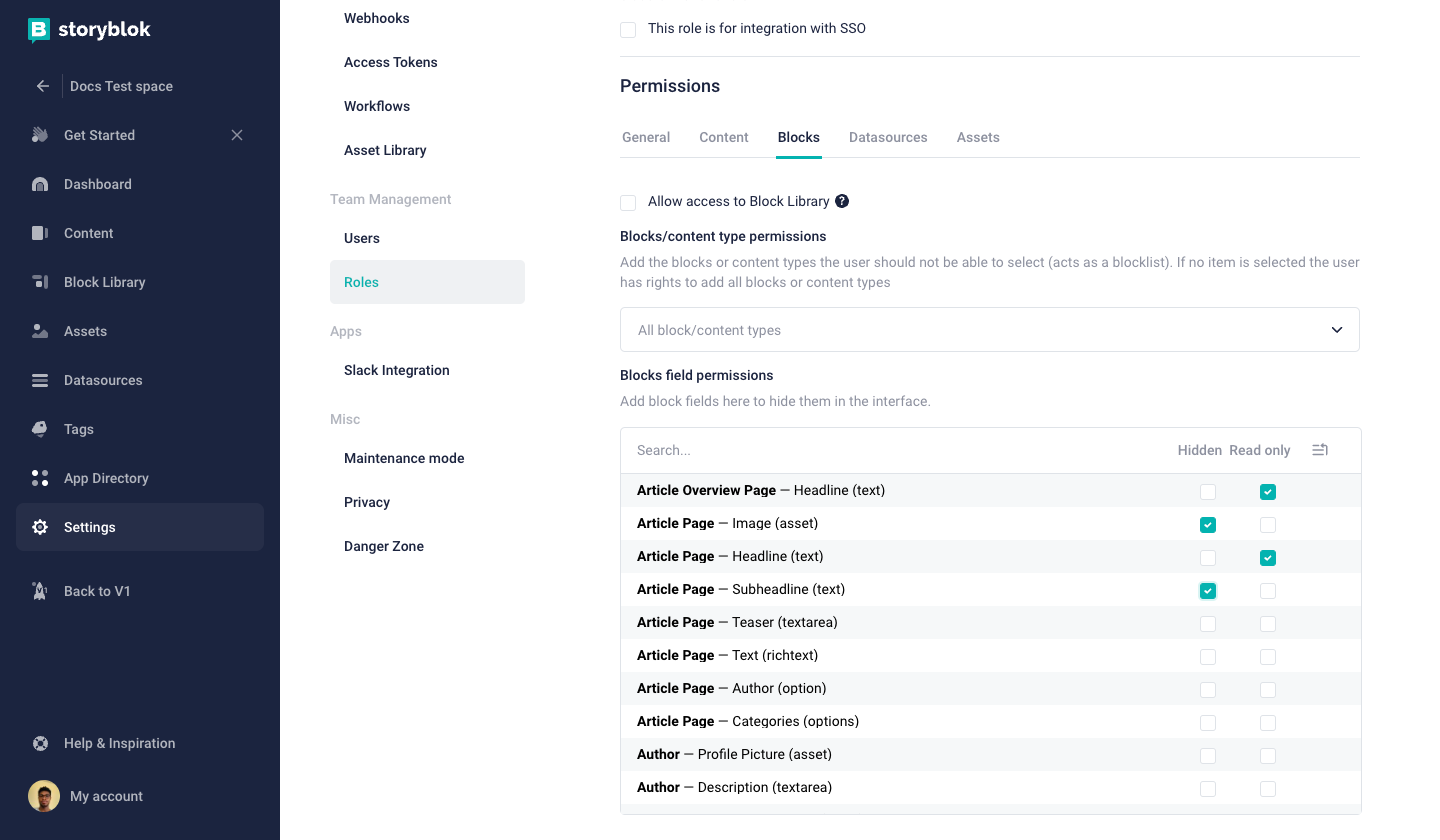
Blocks
Blocks permissions involve granting access to edit specific blocks. Admin is also able to hide certain blocks from specified user Roles.
Datasources
The Datasources category involves permissions to access the key-value pairs within datasources.
Assets
In the Assets category, you can control permissions for editing and uploading assets to specific folders.
Options:
- Select Folders:
- Grant upload access to selected asset folders for this role.
- When selecting a parent folder, its entire tree will be automatically included.
- To select a subfolder, ensure that the parent folder is also selected.
- Hide Restricted Folders:
- Hide assets and asset folders (including their subfolders) that the role doesn't have permission to upload to.
How to create roles
On the left-hand navigation, select {1} Settings, then select {2} Roles and click the {3} Add new role button.
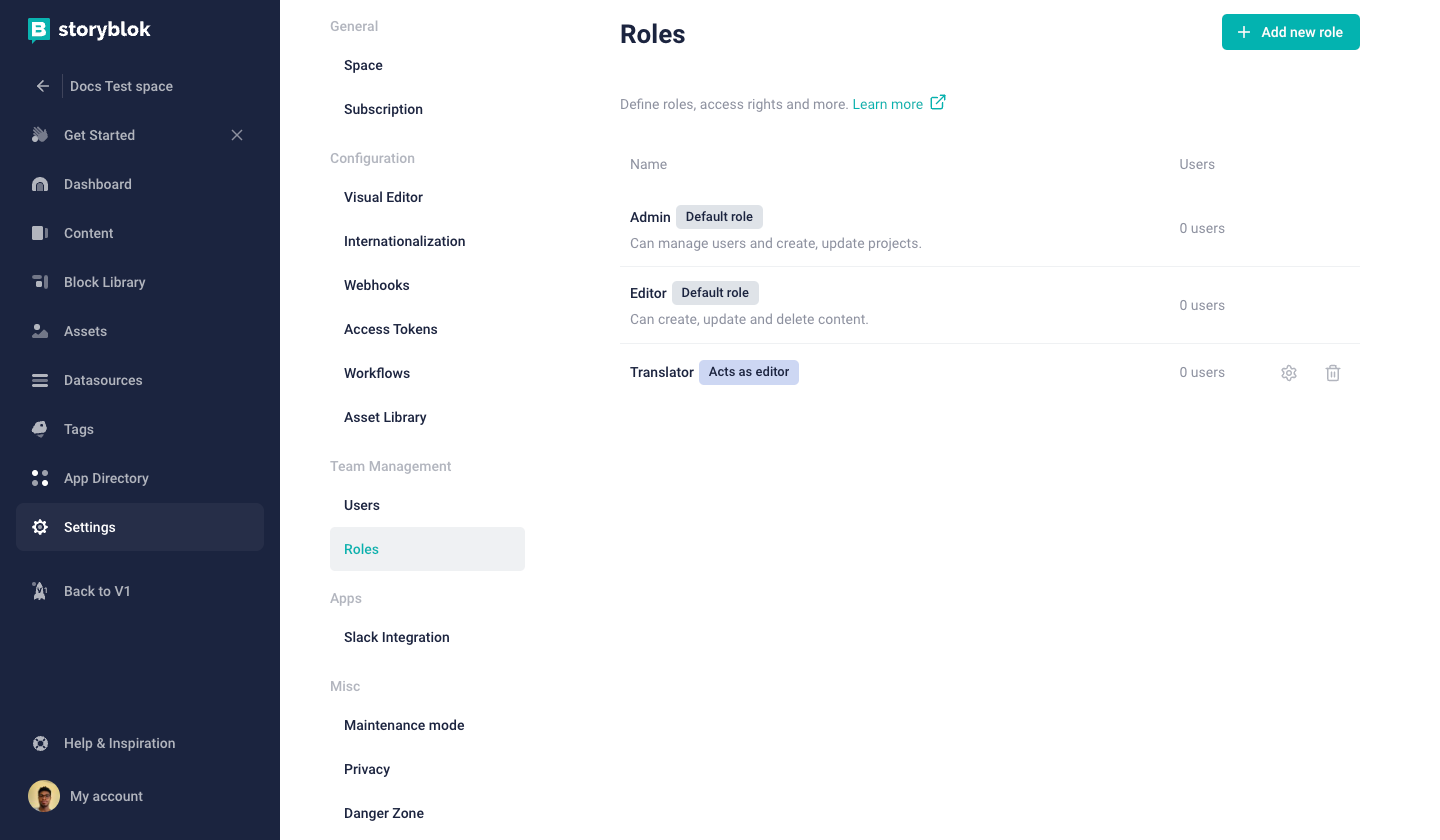
Type in a {1} name for the role, and {2} select your permissions.
Select {3} Save when you are finished.
Adding {4} a short description is optional.
Add {5} if you want to create a role for an SSO user.
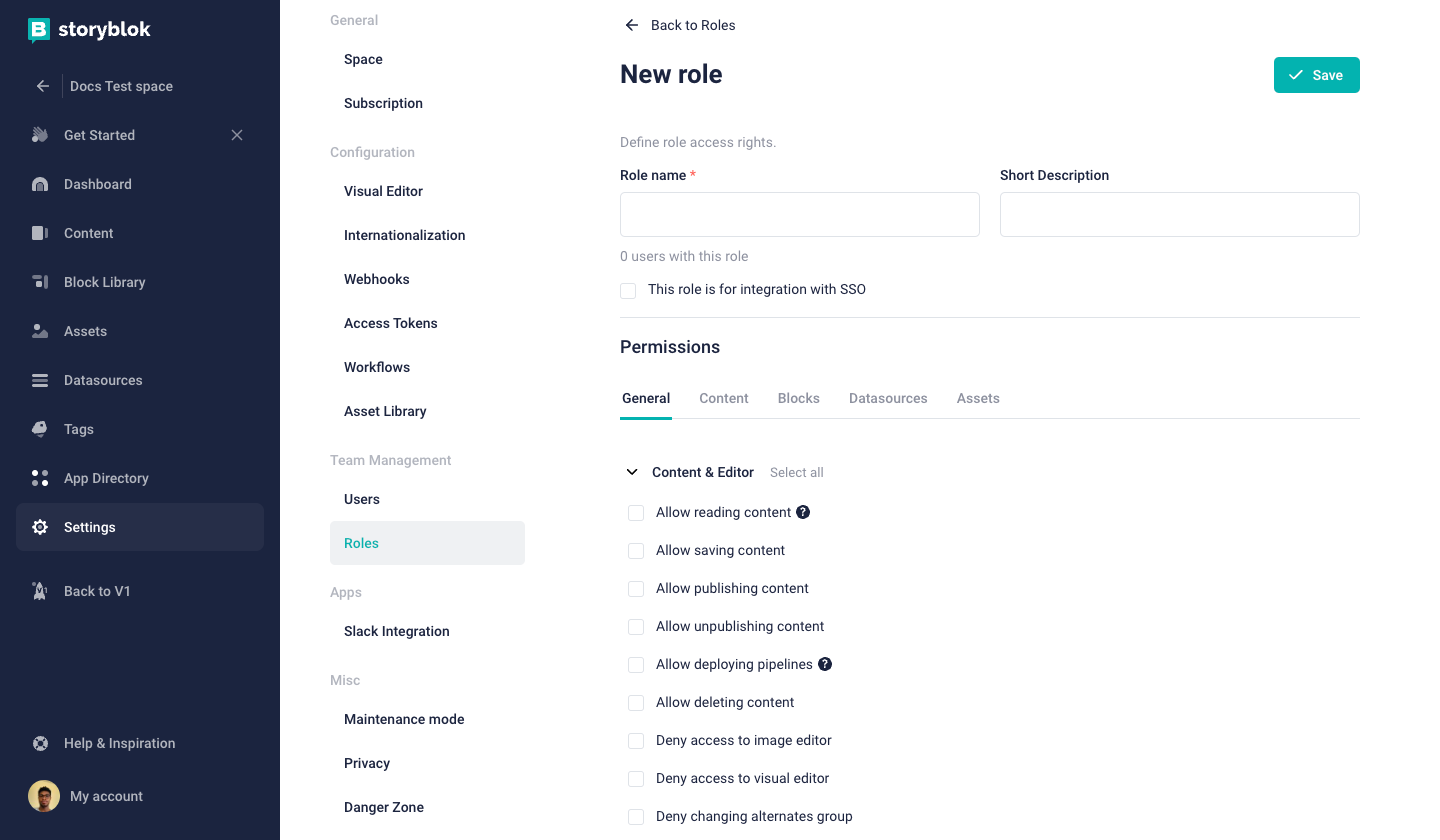
Creating SSO user role
To create a role for a Single Sign-On (SSO), navigate to the roles tab in settings and click on the checkbox for SSO {1}

click the checkbox {1} to indicate this is an SSO role. Next, add the SSO user ID user {2} and click on any checkbox for the default admin {3} or editor {4} user role.
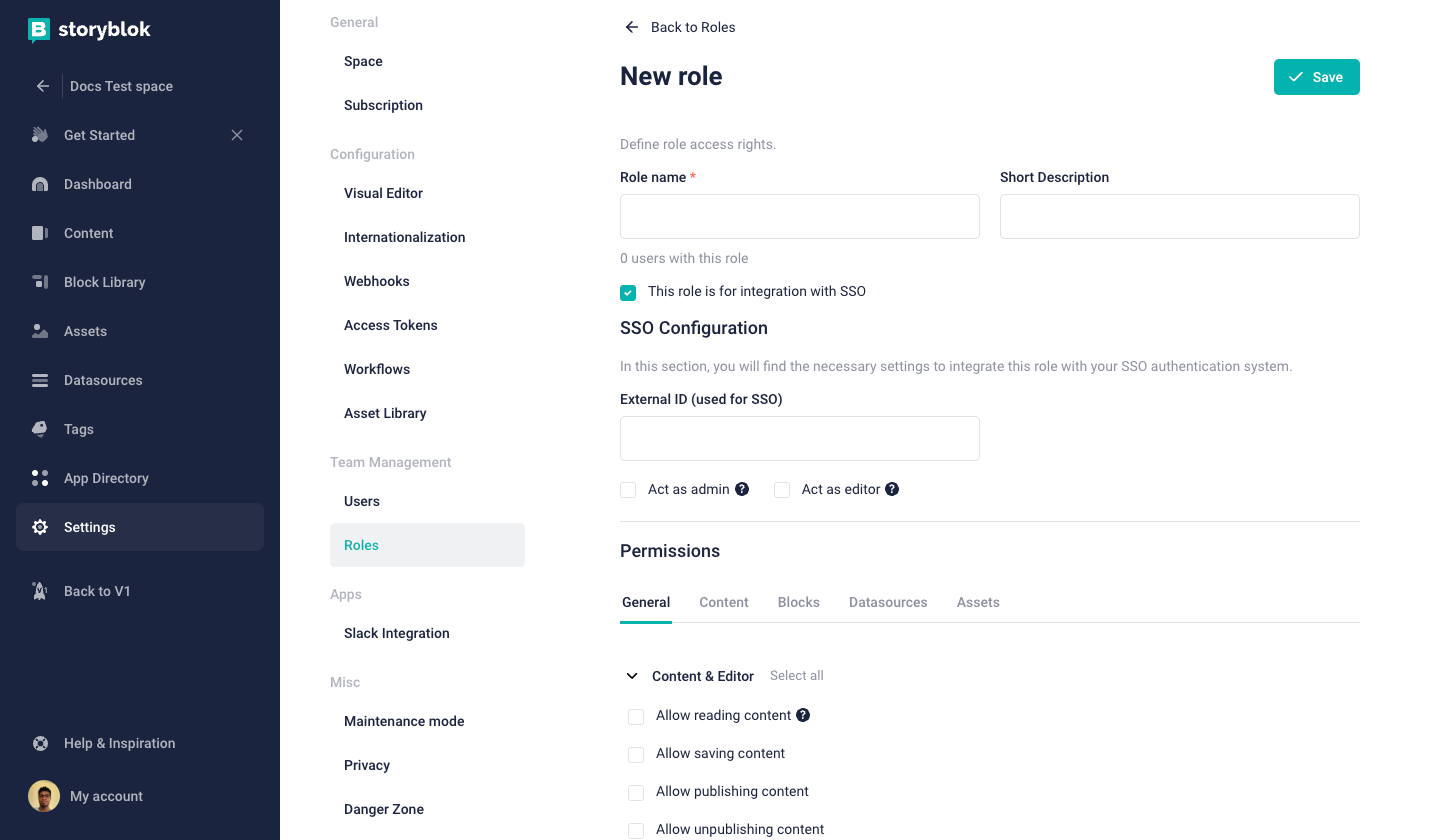
Assign users to roles in a space
To assign a new user to a role in a space, navigate to the Settings {1} tab and click on the Users {2} tab. Next, add a user (opens in a new window) to the space using their username or email address if they are in your Organization (opens in a new window). Next, click on the Choose role {3} dropdown, select a role for the user, and click on the Send invite {4} button to invite them as new users with the assigned roles.
To modify an existing user's role in a space, Click on Settings {1} and click on the Users {2} tab. Next, click on the ellipses of the selected user and click on Edit {3}.
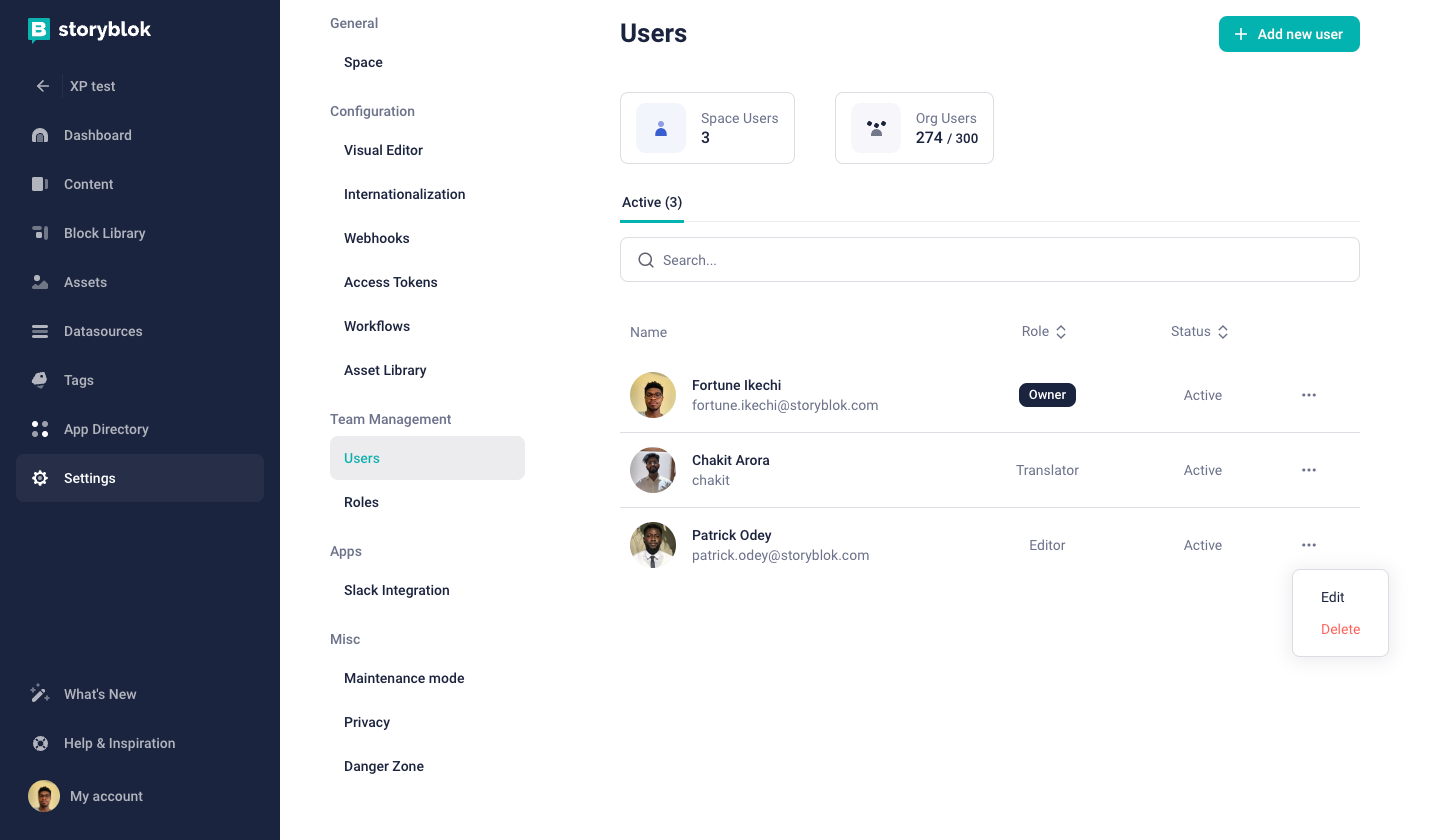
Assign the new role to the user and click Save {1}.
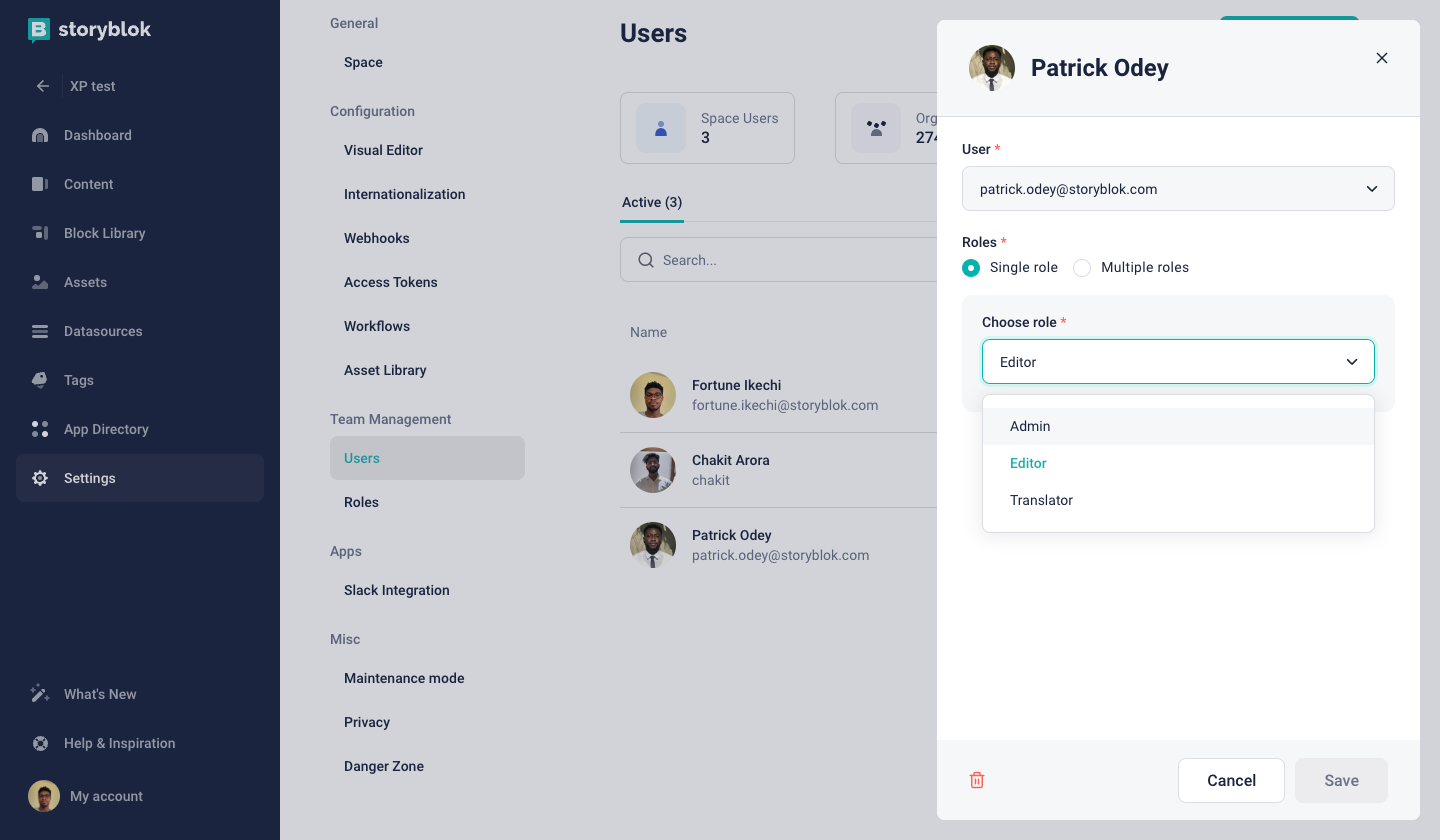
How to change permissions
On the left-hand navigation, select {1} Settings, then select {2} Roles and click on the {3} role you would like to edit.
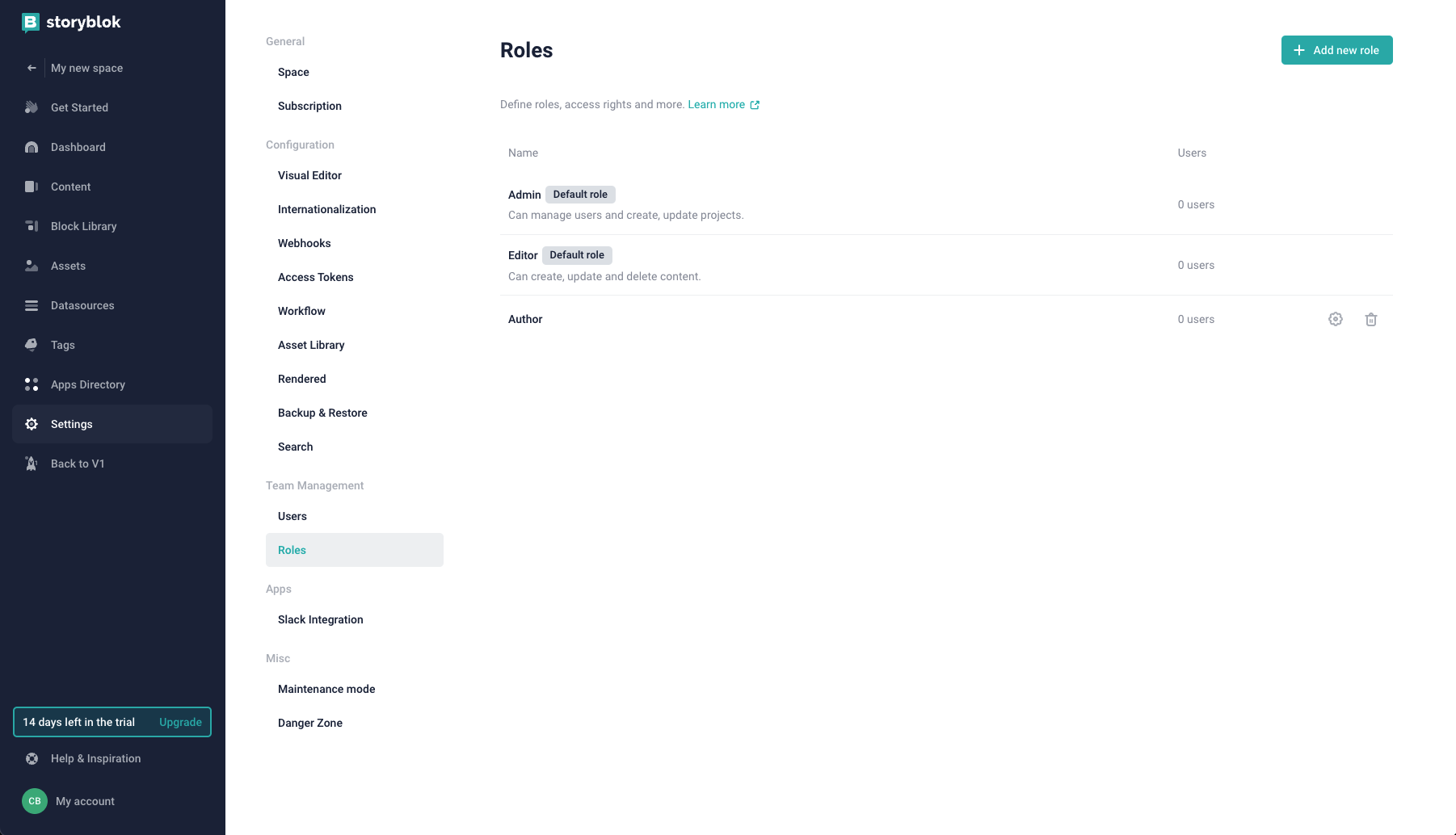
Next, under {1} Permissions, select the {2} category tab from which you wish to edit permissions. {3} Select/deselect your permissions in the expandable lists.
When finished, select {4} Save.
Permission for read-only field access
To set a read-only permission for a field, navigate to your Blocks {1} permissions and click on the Block field permissions {2} dropdown. To make a field read-only for the selected role, click the checkbox {3} next to that field. This will prevent users with this role from editing the field's content.
A collaborator is a person who is an explicit member of your project. As an owner of a space, you can choose between different roles or define your own advanced rights (roles) and permissions.

Roles overview
- Admin
- Space (Read*)
- Story (Create, Read, Update, Delete)
- Component (Create, Read, Update, Delete, Use, Save, Publish)
- Datasource (Create, Read, Update, Delete, Use)
- Datasource Entry (Create, Read, Update, Delete, Use)
<sub>* Is allowed to see it in the space overview - does not have access to the dashboard.</sub>
- Editor
- Space (Read*)
- Story (Create, Read, Update, Delete, Save, Publish)
- Component (Use in SideBySide Editor)
- Datasource (Read)
- Datasource Entry (Read, Update the value's, Export)
<sub>* Is allowed to see it in the space overview - does not have access to the dashboard.</sub><br>
- Advanced Roles
By default, with Advanced Roles, your Collaborator won't be able to do anything with your space. You can add manage rights by clicking on the permission checkboxes in your 'Settings' menu of the role.